Assistant Professor of Computer Science
Director of Public Opinion Analytics

- Email: Reza.Sadeghi@marist.edu
- Online profiles:
BIO
Dr. Reza Sadeghi is the Director of Public Opinion Analytics, Marist Poll and an Assistant Professor of Computer Science at Marist College. Before Marist College, he experienced lectureing various Applied Data Science and Computer Science courses at four higher eduction institute of Sacred Heart University, University of New Haven, Bay Path University, and Providence College. Dr. Sadeghi received his PhD in Computer Science from Wright State University. His main specialty is machine learning, and he loves to research in the fields of health care, Web, and learning analytics. Throughout his PhD, he was a graduate research assistant in the Data Science for Healthcare Lab. He was also research trainee at the division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders at Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School. He contributes to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), and the American Thoracic Society (ATS).
Office_Hourse
- Fall 2025 at Hancock Center 3040, Main Campus, Marist College
- Office Hours Recommended for Public Opinion Analytical GroupTuesday 3:00 PM-5:00PM
- Office Hours Recommended for CMPT 308N-200Wednesday 02:00 PM-3:00PM
- Notice: Students must contact me through my academic email at least 24 hours ahead to schedule a 15-minute appointment.
Teaching
- Fall 2025
- CMPT 308N, Database Management (Section 200)
- Spring 2025
- DATA-220L, Introduction to Data Analysis (Section 112)
- CMPT 308N, Database Management (Section 111)
- DATA-492L, Deep Learning (Section 816)
- MSCS-612N, Deep Learning (Section 816)
- MSIS 537L, Database Management I (Section 800)
- MSCS 542L, Database Management Systems (Section 816)
- Fall 2024
- CMPT 120L, Introduction to Programming (Section 114)
- CMPT 308N, Database Management (Section 201)
- DATA-440L, Machine Learning (Section 192)
- MSIS 537L, Database Management I (Section 537)
- MSCS 542L, Database Management Systems (Section 256)
- Samples of student final projects in the above course:
- Contac Management System using Python & MySQL
- Warehouse Management System using Python & MySQL
- Task Management System by Python
- Spring 2024
- CMPT 120L, Introduction to Programming (Section 112)
- CMPT 308N, Database Management (Section 111)
- DATA-492L, Deep Learning (Section 200)
- MSIS 537L, Database Management I (Section 537)
- MSCS 542L, Database Management Systems (Section 256)
- Samples of student final projects in the above course:
- Task Management System using Python
- Goal Journal Management System using Python
- Diary Management System by MySQL & Python
- Fall 2023
- CMPT 120L, Introduction to Programming (Section 114)
- CMPT 308N, Database Management (Section 113)
- CMPT 308N, Database Management (Section 201)
- MSCS 542L, Database Management Systems (Section 256)
- Samples of student final projects in the above course:
- Task Management System using Python
- Spring 2023
- CMPT 120L, Introduction to Programming (Section 112)
- CMPT 308N, Database Management (Section 111)
- MSCS 542L, Database Management Systems (Section 256)
- CS 617, Artificial Intelligence (Section A)
- Samples of student final projects in the above courses:
- College Data Management System
- Fall 2022
- CMPT 120L, Introduction to Programming (Section 114)
- CMPT 308N, Database Management (Section 200)
- MSCS 542L, Database Management Systems (Section 256)
- CS 617, Artificial Intelligence (Section A)
- CS 617, Artificial Intelligence (Section B)
- Samples of student final projects in the above courses:
- Task Management System using Python & comma-separated values files
- Contact Management System using MySQL & Node.js
- Classification of Edible/Non-Edible Mushrooms using AI algorithms
- Late Spring 2022
- CS 504, Introduction to Programming Using Scripting (Section D)
- CS 551, Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming with Java (Section B)
- CS 603, Advance Database Design (Section D)
- CS 617, Artificial Intelligence (Section A)
- CS 617, Artificial Intelligence (Section B)
- Samples of student final projects in the above courses:
- Phone Book Management System using Python & comma-separated values files
- Spring 2022
- CS 112, Data Structures (Section B)
- CS 504, Introduction to Programming Using Scripting (Section C)
- CS 552, Windows Interface Design (Section C)
- CS 603, Advance Database Design (Section B)
- CS 603, Advance Database Design (Section C)
- CS 617, Artificial Intelligence (Section C)
- Samples of student final projects in the above courses:
- Diary Management System using MySQL & XAMPP
- Contact Management System using MySQL & Python
- Game Application Rating Prediction in Jupyter Notebook
- Summer 2021
- ADS654, Deep Learning (Section Z1)
- Spring 2021
- CSCI 1110, Introduction to C Programming (Section 01)
- CSCI 1110, Introduction to C Programming (Section 02)
- CSCI 1110, Introduction to C Programming (Section 03)
- CSCI 2210, Java Programming (Section 01)
- CSCI 6622/2215, Database Systems/Databases and SQL (Section 01)
- ADS650, Time Series Analysis (Section Z1)
- Samples of student final projects in the above courses:
- Warehouse Management System in C
- Task Management System by Java & MySQL
- Java Warehouse Management System
- Grocery Management System using MySQL & Python
- Library Management System by MySQL & Python
- Fall 2020
- CSC 103, Intro to Computer Science (Section 01)
- CSCI 1110, Introduction to C Programming (Section 05)
- CSCI 1110, Introduction to C Programming (Section 06)
- CSCI 3351, Script Programming/Python (Section 01)
- CSCI 6674/4454, Special Topic:Data Mining (Section 01)
- Samples of student final projects in the above courses:
- Calendar Management System in C
- Library Management System in C
- Django python student resume platform
- Django python jewelry store website
- Breast cancer prediction using machine learning
- Predicting the 5-year career longevity of the NBA Rookies
Research Groups
Current Research

|
Machine learning for healthcare
 Stable and accurate clinical decision support systems are essential tools for providing fast diagnosis and high quality treatment
of healthcare issues. Such systems are effective as they rely on the risk factors of health issues and are validated over
big healthcare data. Machine learning techniques can both extract the risk factors from electronic health records and
bring light to complex relationships among the risk factors. Along this theme, I employed distinct machine learning methodologies
as simple as logistic regression up to convolutional neural network and probabilistic graphical models to
estimate sleep quality,
manage dementia,
identify disease risk factors,
assess alcohol withdrawal,
and predict early hospital mortality.
Stable and accurate clinical decision support systems are essential tools for providing fast diagnosis and high quality treatment
of healthcare issues. Such systems are effective as they rely on the risk factors of health issues and are validated over
big healthcare data. Machine learning techniques can both extract the risk factors from electronic health records and
bring light to complex relationships among the risk factors. Along this theme, I employed distinct machine learning methodologies
as simple as logistic regression up to convolutional neural network and probabilistic graphical models to
estimate sleep quality,
manage dementia,
identify disease risk factors,
assess alcohol withdrawal,
and predict early hospital mortality.
|

|
Web mining
 World Wide Web (WWW) is the biggest source of available information.
Web mining tries to extract desired data from this massive information in an efficient way.
The information is retrieved from three distinguished levels of content, structure, and usage
of accessible documents. From the perspective of web content mining, efficient algorithms can
convert huge source of texts, images, sounds, and videos into usable information.
However, each source of information implies different concepts in distinct context.
As a result, separating the accessible documents into distinguished categories,
known as web structure mining, is essential. The speed of producing new information
is too fast such that expert knowledge is not enough to categorize the huge amount of WWW information.
One of the best methods to address this issue is to consider the navigational behavior of users
known as web usage mining. I am following these three web mining levels
through text mining, web robots, and web structure characterization.
World Wide Web (WWW) is the biggest source of available information.
Web mining tries to extract desired data from this massive information in an efficient way.
The information is retrieved from three distinguished levels of content, structure, and usage
of accessible documents. From the perspective of web content mining, efficient algorithms can
convert huge source of texts, images, sounds, and videos into usable information.
However, each source of information implies different concepts in distinct context.
As a result, separating the accessible documents into distinguished categories,
known as web structure mining, is essential. The speed of producing new information
is too fast such that expert knowledge is not enough to categorize the huge amount of WWW information.
One of the best methods to address this issue is to consider the navigational behavior of users
known as web usage mining. I am following these three web mining levels
through text mining, web robots, and web structure characterization.
|
|
Structure learning
 Learning Bayesian network structures from data is a NP hard problem
since the number of candidate graphs grows super-exponentially.
Through this research, the meaningful structure of data is investigated
to discover unknown relations in biomedical fields.
This research utilizes both advantages of constant-based and score-based
methods. Bayesian network learning is commonly executed as structure learning
and parameter learning, respectively. The structure learning point to learn
the structure of a directed acyclic graph. However, the parameter learning tries
to address learning the local distribution showed by the structure of learned
directed acrylic graph via the structure learning. Both learning stages can handle
by unsupervised and supervised learning methods.
Learning Bayesian network structures from data is a NP hard problem
since the number of candidate graphs grows super-exponentially.
Through this research, the meaningful structure of data is investigated
to discover unknown relations in biomedical fields.
This research utilizes both advantages of constant-based and score-based
methods. Bayesian network learning is commonly executed as structure learning
and parameter learning, respectively. The structure learning point to learn
the structure of a directed acyclic graph. However, the parameter learning tries
to address learning the local distribution showed by the structure of learned
directed acrylic graph via the structure learning. Both learning stages can handle
by unsupervised and supervised learning methods.
|
Past Research
|
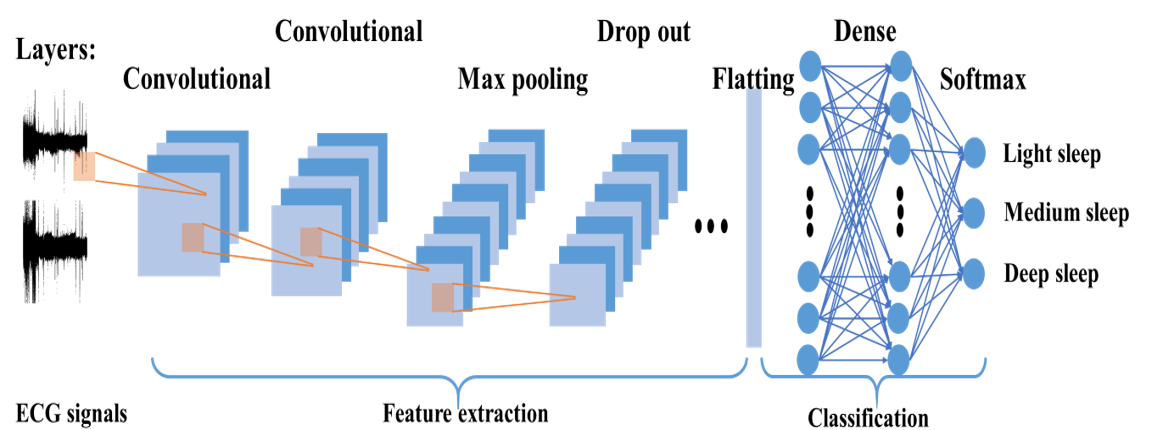
Sleep quality prediction using heart rate variability
 We employed machine learning techniques to enhance sleep quality prediction by selecting more effective features
and reducing the dependability to the expert knowledge in feature computation.
We designed several sleep quality methodologies by applying a great range of machine learning techniques over
electronic health records, heart rate variability (HRV) features, and the raw Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals.
In the process of predicting sleep quality from HRV,
we came up with a clinical decision support system that processes the raw electrocardiogram signals
independently from the prior knowledge of sleep experts.
This system employs a convolutional neural network (CNN) to predict sleep quality
based on heart activities during each night by analyzing images of two ECG signals during Polysomnography studies.
To our knowledge, this is one of the first studies to predict sleep quality using HRV.
The detailed report of this research is provided in “Predicting sleep quality in osteoporosis patients using electronic health records and heart rate variability”,
which is presented in 42nd IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC2020).
We employed machine learning techniques to enhance sleep quality prediction by selecting more effective features
and reducing the dependability to the expert knowledge in feature computation.
We designed several sleep quality methodologies by applying a great range of machine learning techniques over
electronic health records, heart rate variability (HRV) features, and the raw Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals.
In the process of predicting sleep quality from HRV,
we came up with a clinical decision support system that processes the raw electrocardiogram signals
independently from the prior knowledge of sleep experts.
This system employs a convolutional neural network (CNN) to predict sleep quality
based on heart activities during each night by analyzing images of two ECG signals during Polysomnography studies.
To our knowledge, this is one of the first studies to predict sleep quality using HRV.
The detailed report of this research is provided in “Predicting sleep quality in osteoporosis patients using electronic health records and heart rate variability”,
which is presented in 42nd IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC2020).
|
|
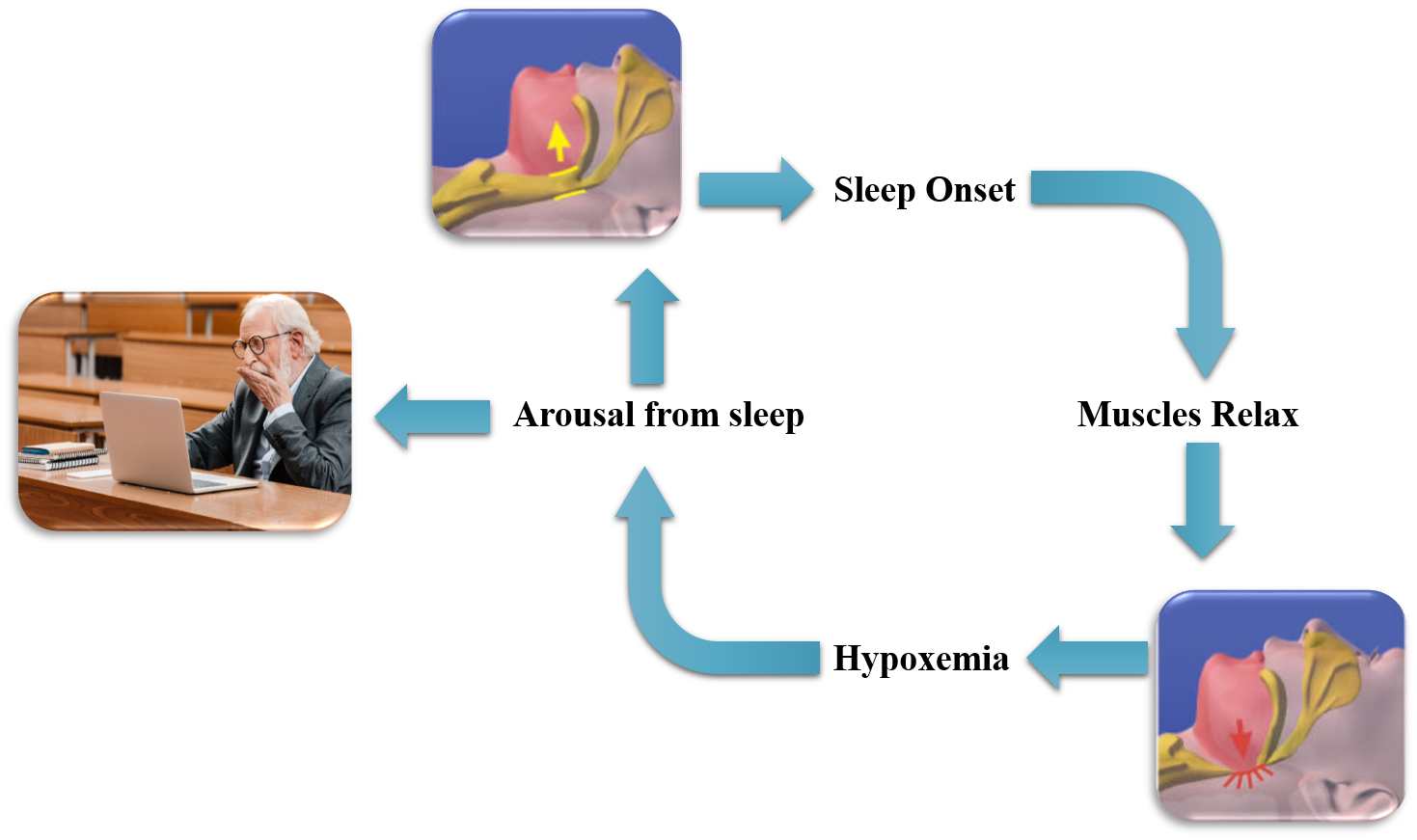
Identifying the disease-specific risk factors of daytime sleepiness  Abnormal sleep quality or sleep quantity causes excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS),
which is a highly prevalent condition in the older adult society.
EDS is a symptom of several diseases, such as neurological disorders, e.g. dementia, and sleep breathing disorders,
e.g. apnea. Distinguishing disease-specific risk factors of EDS can both reveal underlying reasons of abnormal sleep quality
and enhance its prediction. To do so, we investigated EDS risk factors in two groups of patients one group with
and one group without severe sleep apnea. The report of this research has been reflected in “Sleep Propensity and Sleep Apnea-Specific Hypoxia Are Associated with Excessive Daytime Sleepiness”
and presented at Annals of the American Thoracic Society (ATS2020).
Abnormal sleep quality or sleep quantity causes excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS),
which is a highly prevalent condition in the older adult society.
EDS is a symptom of several diseases, such as neurological disorders, e.g. dementia, and sleep breathing disorders,
e.g. apnea. Distinguishing disease-specific risk factors of EDS can both reveal underlying reasons of abnormal sleep quality
and enhance its prediction. To do so, we investigated EDS risk factors in two groups of patients one group with
and one group without severe sleep apnea. The report of this research has been reflected in “Sleep Propensity and Sleep Apnea-Specific Hypoxia Are Associated with Excessive Daytime Sleepiness”
and presented at Annals of the American Thoracic Society (ATS2020).
|
|
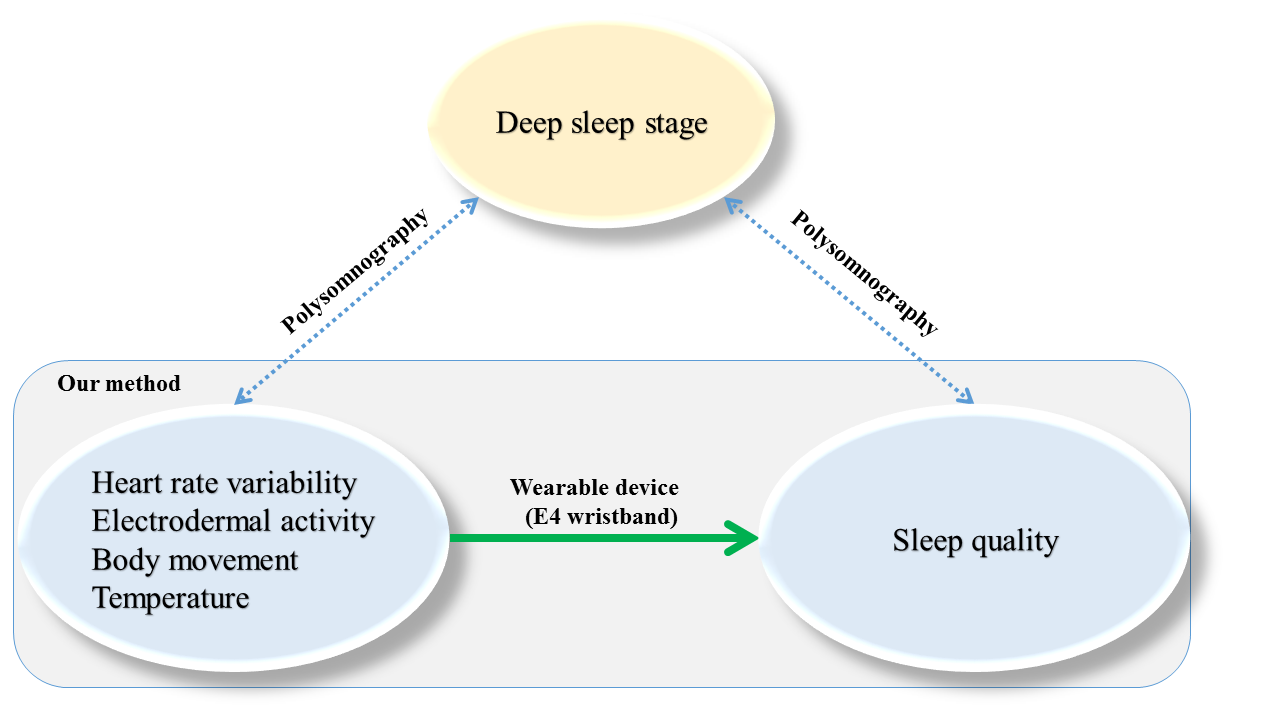
Sleep quality prediction in caregivers of people with dementia  Most caregivers of people with dementia (CPWD) experience a high degree of stress due to the demands of providing care,
especially when addressing unpredictable behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia.
Such challenging responsibilities make caregivers susceptible to poor sleep quality with detrimental effects on their overall health.
Hence, monitoring caregivers’ sleep quality can provide important CPWD stress assessment.
Most current sleep studies are based on polysomnography, which is expensive and potentially disrupts the caregiving routine.
To address these issues, we propose a clinical decision support system to predict sleep quality based on
trends of physiological signals in the deep sleep stage. This research has been elaborated on “Sleep quality prediction in caregivers using physiological signals” (Presentation slides / Source code)
and published in Computers in Biology and Medicine.
It is also featured in Using the E4 to assess sleep in caregivers of people with dementia.
Most caregivers of people with dementia (CPWD) experience a high degree of stress due to the demands of providing care,
especially when addressing unpredictable behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia.
Such challenging responsibilities make caregivers susceptible to poor sleep quality with detrimental effects on their overall health.
Hence, monitoring caregivers’ sleep quality can provide important CPWD stress assessment.
Most current sleep studies are based on polysomnography, which is expensive and potentially disrupts the caregiving routine.
To address these issues, we propose a clinical decision support system to predict sleep quality based on
trends of physiological signals in the deep sleep stage. This research has been elaborated on “Sleep quality prediction in caregivers using physiological signals” (Presentation slides / Source code)
and published in Computers in Biology and Medicine.
It is also featured in Using the E4 to assess sleep in caregivers of people with dementia.
|

|
Alcohol withdrawal prediction  By the definition of the World Health Organization, alcohol use disorder refers to any form of alcohol consumption that causes
health problems. Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome (AWS) occurs roughly 4 to 72 hours following cessation or reduction of prolonged,
heavy alcohol ingestion. Withdrawal delirium or Delirium Tremens is considered the most dangerous symptom of AWS which can lead to
the death. During the initial 8 hours after the last drink, patients face with anxiety, insomnia, nausea, and abdominal pain.
This condition is followed by high blood pressure, increased body temperature, unusual heart rate, and confusion.
If this syndrome does not receive any treatment, the patients will suffer from hallucinations, fever, seizures, and agitation.
As a result, there is an essential need to predict and treat this syndrome in the initial stages.
The outcomes of this research are described in “Predicting alcohol withdrawal in intensive care units”
and presented at The Symposium of Student Research, Scholarship, and Creative Activities 2020.
By the definition of the World Health Organization, alcohol use disorder refers to any form of alcohol consumption that causes
health problems. Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome (AWS) occurs roughly 4 to 72 hours following cessation or reduction of prolonged,
heavy alcohol ingestion. Withdrawal delirium or Delirium Tremens is considered the most dangerous symptom of AWS which can lead to
the death. During the initial 8 hours after the last drink, patients face with anxiety, insomnia, nausea, and abdominal pain.
This condition is followed by high blood pressure, increased body temperature, unusual heart rate, and confusion.
If this syndrome does not receive any treatment, the patients will suffer from hallucinations, fever, seizures, and agitation.
As a result, there is an essential need to predict and treat this syndrome in the initial stages.
The outcomes of this research are described in “Predicting alcohol withdrawal in intensive care units”
and presented at The Symposium of Student Research, Scholarship, and Creative Activities 2020.
|
|
Mortality Prediction  Early hospital mortality prediction is critical as intensivists strive to make efficient medical decisions
about the severely ill patients staying in intensive care units. As a result, various methods have been developed
to address this problem based on clinical records. However, some of the laboratory test results are time-consuming
and need to be processed. To address this issue, we proposed a novel method to predict mortality using features extracted from
the heart signals of patients within the first hour of ICU admission. In order to predict the risk, quantitative features
have been computed based on the heart rate signals of ICU patients. Outcomes of the experiments indicates that heart rate signals
can be used for predicting mortality in patients in the ICU, achieving a comparable performance with existing predictions that rely
on high dimensional features from clinical records which need to be processed and may contain missing information.
The outcomes of this research are reported in “Early Hospital Mortality Prediction using Vital Signals” (Presentation slides / Source code)
and has been accepted in IEEE/ACM CHASE 2018 and published in the journal of Smart Health.
Early hospital mortality prediction is critical as intensivists strive to make efficient medical decisions
about the severely ill patients staying in intensive care units. As a result, various methods have been developed
to address this problem based on clinical records. However, some of the laboratory test results are time-consuming
and need to be processed. To address this issue, we proposed a novel method to predict mortality using features extracted from
the heart signals of patients within the first hour of ICU admission. In order to predict the risk, quantitative features
have been computed based on the heart rate signals of ICU patients. Outcomes of the experiments indicates that heart rate signals
can be used for predicting mortality in patients in the ICU, achieving a comparable performance with existing predictions that rely
on high dimensional features from clinical records which need to be processed and may contain missing information.
The outcomes of this research are reported in “Early Hospital Mortality Prediction using Vital Signals” (Presentation slides / Source code)
and has been accepted in IEEE/ACM CHASE 2018 and published in the journal of Smart Health.
|
|
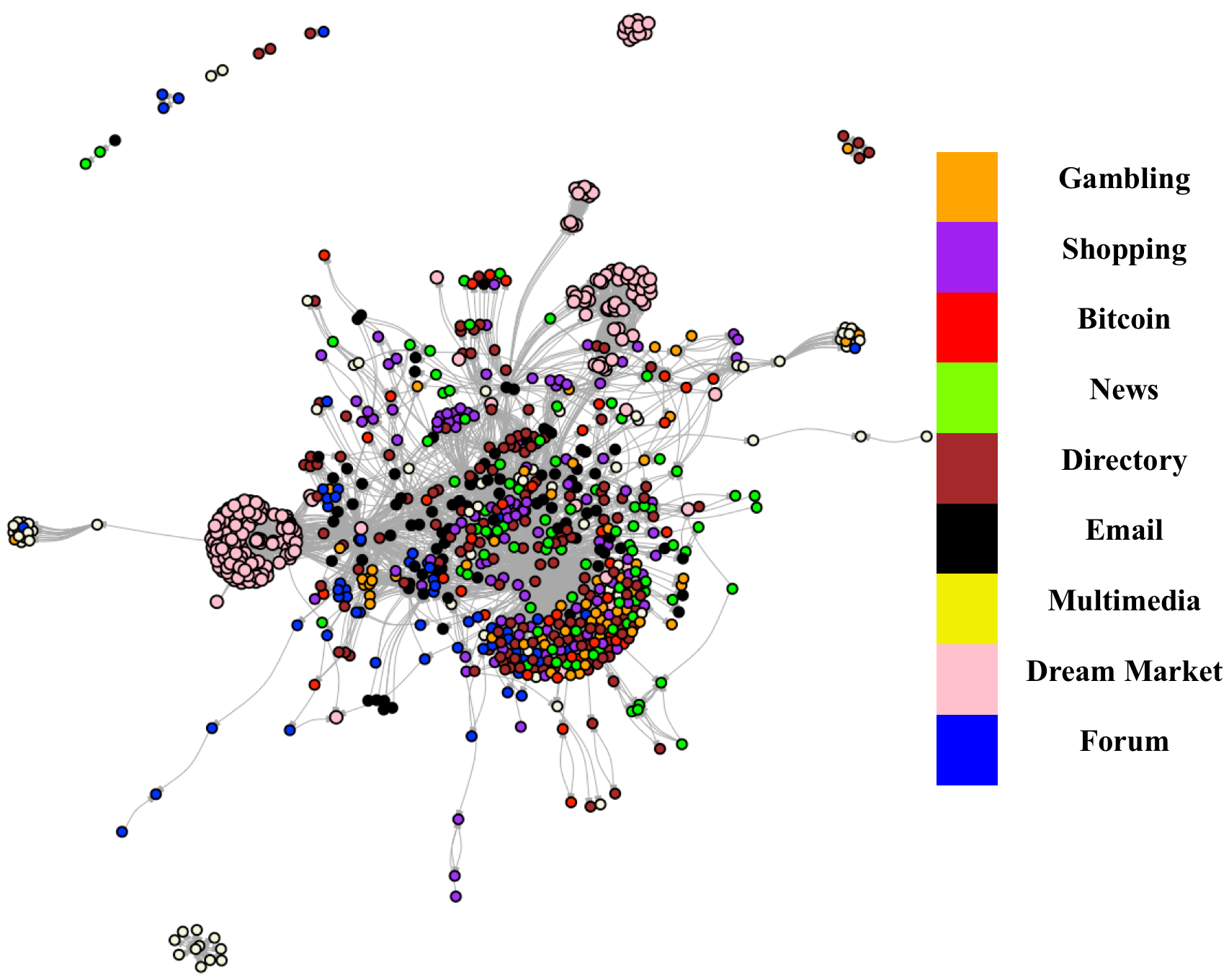
Tor structure characterization  Tor is among most well-known dark net in the world. It has noble uses, including as a platform for free speech and information
dissemination under the guise of true anonymity, but may be culturally better known as a conduit for
criminal activity and as a platform to market illicit goods and data.
Past studies on the content of Tor support this notion, but were carried out by targeting popular domains
likely to contain illicit content. A survey of past studies may thus not yield a complete evaluation of the content
and use of Tor. This work addresses this gap by presenting a broad evaluation of the content of the English Tor ecosystem.
The outcomes of this research are reported in “A Broad Evaluation of the Tor English Content Ecosystem”
and “Interaction of Structure and Information on Tor”
is presented in "10th ACM Conference on Web Science" and "COMPLEX NETWORKS 2020", respectively.
Tor is among most well-known dark net in the world. It has noble uses, including as a platform for free speech and information
dissemination under the guise of true anonymity, but may be culturally better known as a conduit for
criminal activity and as a platform to market illicit goods and data.
Past studies on the content of Tor support this notion, but were carried out by targeting popular domains
likely to contain illicit content. A survey of past studies may thus not yield a complete evaluation of the content
and use of Tor. This work addresses this gap by presenting a broad evaluation of the content of the English Tor ecosystem.
The outcomes of this research are reported in “A Broad Evaluation of the Tor English Content Ecosystem”
and “Interaction of Structure and Information on Tor”
is presented in "10th ACM Conference on Web Science" and "COMPLEX NETWORKS 2020", respectively.
|
|
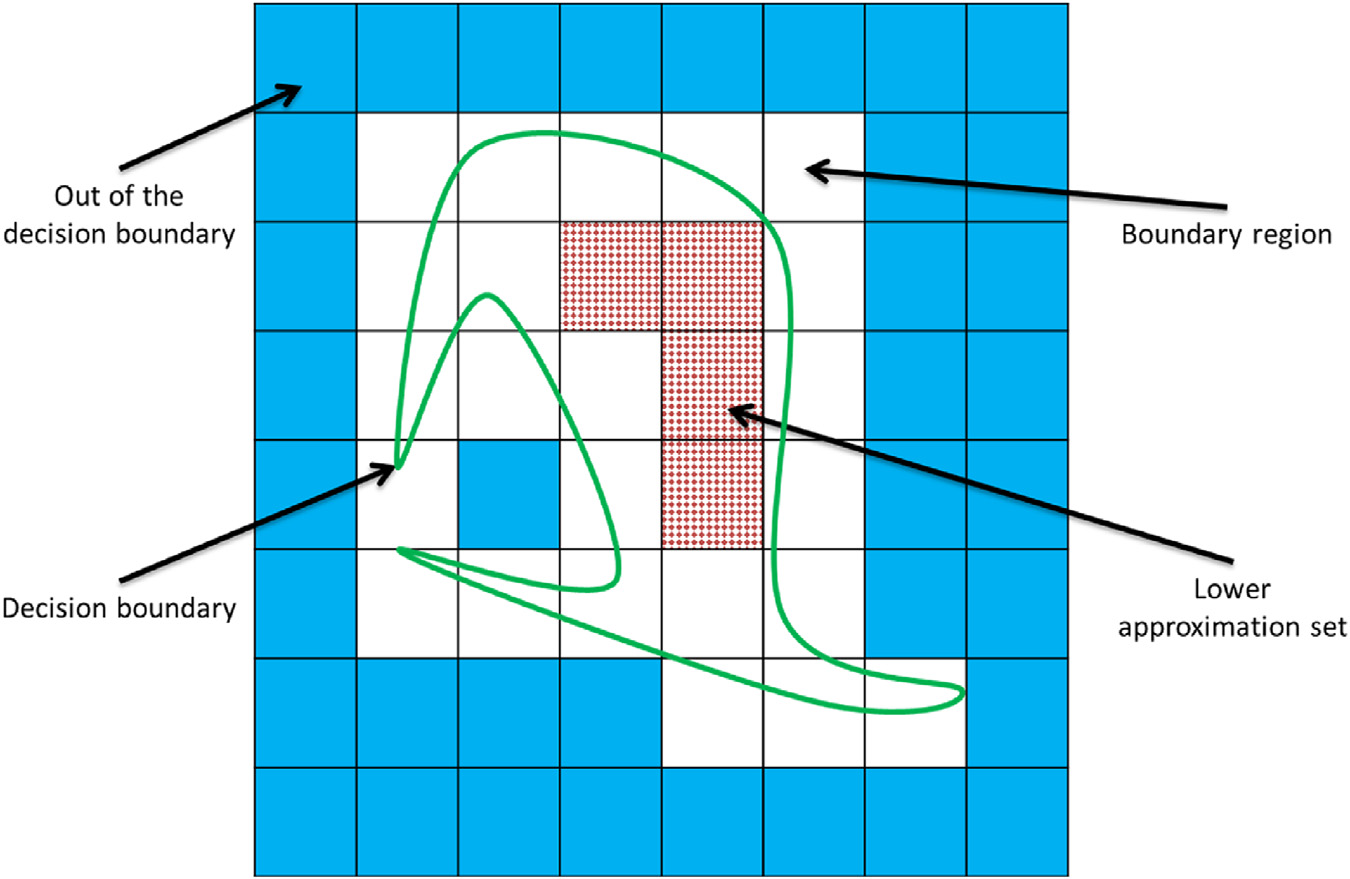
Web Robot Detection  The accurate detection of web robot sessions from a web server log is essential to take accurate traffic-
level measurements and to protect the performance and privacy of information on a Web server. Moreover,
the irrecoverable risks of visits from malicious robots that intentionally try to evade web server
intrusion detection systems, covering-up their visits with fabricated fields in their http r
est packets,
cannot be ignored. To separate both types of robots from humans in practice, analysts turn to heuristic
methods or state-of-the-art soft computing approaches that have only been tuned to the specification of
a kind of web server. Noting that the landscape of web robot agents is ever changing, and that behavioral
patterns and characteristics vary across different web servers, both options are lacking. To overcome this
challenge, my colleagues and I proposed several methods based on Fuzzy Rough Set, Markov Clustering, Self-organizing Map concepts.
The report of this research is reflected in “A soft computing approach for benign and malicious web robot detection” (Source code) and
“Detection of Web site visitors based on fuzzy rough sets” published in Expert Systems with Applications journals (Impact factor: 3.928) and Soft Computing (Impact factor: 2.472), respectively.
The accurate detection of web robot sessions from a web server log is essential to take accurate traffic-
level measurements and to protect the performance and privacy of information on a Web server. Moreover,
the irrecoverable risks of visits from malicious robots that intentionally try to evade web server
intrusion detection systems, covering-up their visits with fabricated fields in their http r
est packets,
cannot be ignored. To separate both types of robots from humans in practice, analysts turn to heuristic
methods or state-of-the-art soft computing approaches that have only been tuned to the specification of
a kind of web server. Noting that the landscape of web robot agents is ever changing, and that behavioral
patterns and characteristics vary across different web servers, both options are lacking. To overcome this
challenge, my colleagues and I proposed several methods based on Fuzzy Rough Set, Markov Clustering, Self-organizing Map concepts.
The report of this research is reflected in “A soft computing approach for benign and malicious web robot detection” (Source code) and
“Detection of Web site visitors based on fuzzy rough sets” published in Expert Systems with Applications journals (Impact factor: 3.928) and Soft Computing (Impact factor: 2.472), respectively.
|
|
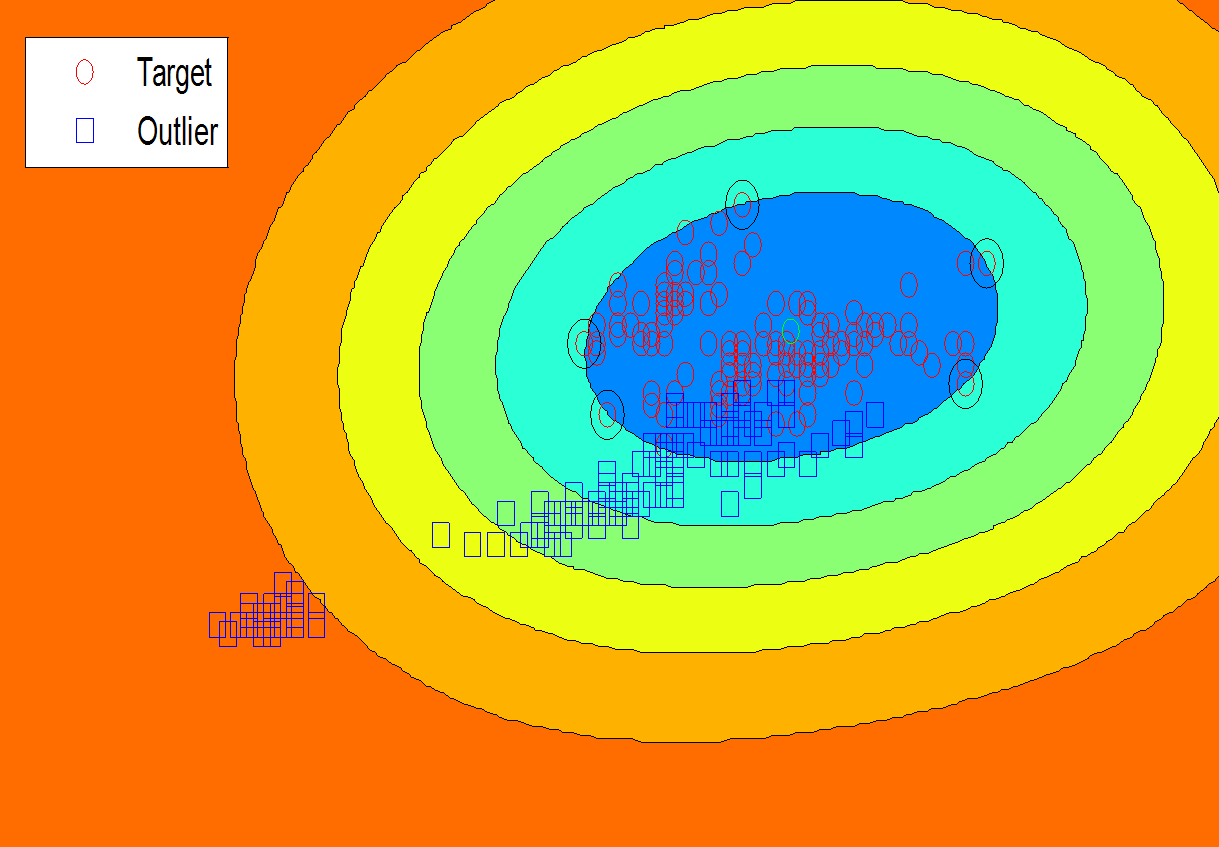
Outlier Detection  Event handlers have wide range of applications
such as medical assistant systems and fire suppression systems.
These systems try to provide accurate responses based
on the least information. Support vector data description
(SVDD) is one of the appropriate tools for such detections,
which should handle lack of information. Therefore, many
efforts have been done to improve SVDD. Unfortunately,
the existing descriptors suffer from weak data characteristic
in sparse data sets and their tuning parameters are organized
improperly. These issues cause reduction of accuracy in event
handlers when they are faced with data shortage. Therefore,
my colleagues and I proposed several methods based on Fuzzy Rough Set, Bat Algorithm, and Chaos theory.
The results of this research is presented in “Weighted support vector data description based on chaotic bat algorithm” and
“Automatic support vector data description” (Source code) published in Applied Soft Computing journals (Impact factor: 3.541) and Soft Computing (Impact factor: 2.472), respectively.
Event handlers have wide range of applications
such as medical assistant systems and fire suppression systems.
These systems try to provide accurate responses based
on the least information. Support vector data description
(SVDD) is one of the appropriate tools for such detections,
which should handle lack of information. Therefore, many
efforts have been done to improve SVDD. Unfortunately,
the existing descriptors suffer from weak data characteristic
in sparse data sets and their tuning parameters are organized
improperly. These issues cause reduction of accuracy in event
handlers when they are faced with data shortage. Therefore,
my colleagues and I proposed several methods based on Fuzzy Rough Set, Bat Algorithm, and Chaos theory.
The results of this research is presented in “Weighted support vector data description based on chaotic bat algorithm” and
“Automatic support vector data description” (Source code) published in Applied Soft Computing journals (Impact factor: 3.541) and Soft Computing (Impact factor: 2.472), respectively.
|
|
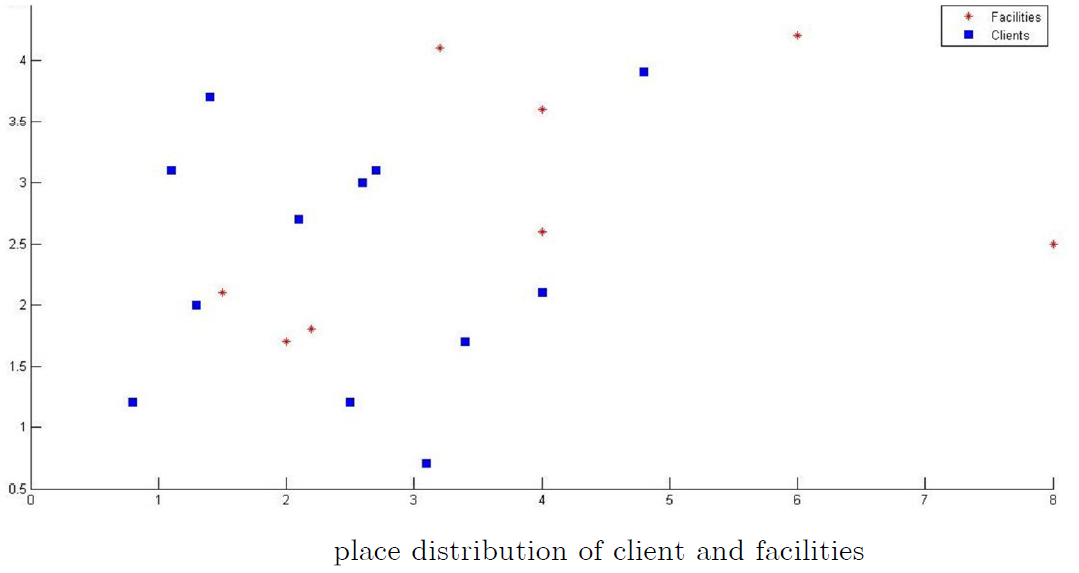
Dynamic Facility Location  Determination of facilities, such as factories or
warehouses, location and availability conditions is one of the
important and strategic decisions for an organization to make.
Transportation costs that form a major part of goods price are
dependent to this decision making. There are verity of methods
have been presented to achieve the optimal locations of these
facilities which are generally deterministic. In real world accurate
estimation of the effective parameters on this optimal location for
single or multiple time periods is difficult and merely impossible.In
this research, my colleagues and I tried to achieve an efficient model with
consideration of uncertainty demand over different time periods on
the basis of previously presented models that we call stochastic
dynamic facilities location problem. In order to do so we use
stochastic constrain programming which convert the stochastic
model to a deterministic one. The results of this research is presented in “Dynamic Facility Location with Stochastic Demand” and
Stochastic Facilities location Model by Using Stochastic Programming” published in Shiraz Journal of System Management.
Determination of facilities, such as factories or
warehouses, location and availability conditions is one of the
important and strategic decisions for an organization to make.
Transportation costs that form a major part of goods price are
dependent to this decision making. There are verity of methods
have been presented to achieve the optimal locations of these
facilities which are generally deterministic. In real world accurate
estimation of the effective parameters on this optimal location for
single or multiple time periods is difficult and merely impossible.In
this research, my colleagues and I tried to achieve an efficient model with
consideration of uncertainty demand over different time periods on
the basis of previously presented models that we call stochastic
dynamic facilities location problem. In order to do so we use
stochastic constrain programming which convert the stochastic
model to a deterministic one. The results of this research is presented in “Dynamic Facility Location with Stochastic Demand” and
Stochastic Facilities location Model by Using Stochastic Programming” published in Shiraz Journal of System Management.
|
|
Job Scheduling  Nowadays the requests of managers and other
persons who benefited by such projects for drop total
project’s cost have increased considerably. Besides,
the amount of changes exert on this factors can result
to variation in initial estimation of them. In this way,
however; by observing this types of changes in
different circumstances, the ideal quality for projects
is going to be considered. Moreover, generally in
realty world, either falling in time consuming or the
amount usage of resources for a task could not lead
to decline of task quality. As a result, assigning fixed
and deterministic values for assessing ideal quality
leading to unpredictable outcomes. I this study,
fuzzy logic developed remarkably to measure the
quality for wide range of tasks and activities in
various variation circumstances. At last, the
presented model apply to real case study and the
obtained values have proved the efficiency of
proposed model in comparison to others in
deterministic situations. The report of this research is reflected in
“Solving the equilibrium problem of time, cost, resource and quality of project network by using expanded fuzzy logic set”.
Nowadays the requests of managers and other
persons who benefited by such projects for drop total
project’s cost have increased considerably. Besides,
the amount of changes exert on this factors can result
to variation in initial estimation of them. In this way,
however; by observing this types of changes in
different circumstances, the ideal quality for projects
is going to be considered. Moreover, generally in
realty world, either falling in time consuming or the
amount usage of resources for a task could not lead
to decline of task quality. As a result, assigning fixed
and deterministic values for assessing ideal quality
leading to unpredictable outcomes. I this study,
fuzzy logic developed remarkably to measure the
quality for wide range of tasks and activities in
various variation circumstances. At last, the
presented model apply to real case study and the
obtained values have proved the efficiency of
proposed model in comparison to others in
deterministic situations. The report of this research is reflected in
“Solving the equilibrium problem of time, cost, resource and quality of project network by using expanded fuzzy logic set”.
|
Selected Publications
- R. Sadeghi, T. Banerjee, J. C. Hughes, & L. W. Lawhorne (2019), “Predicting sleep quality of caregivers using physiological signals”, Computers in Biology and Medicine. (Impact factor: 2.115) [Presentation slides / Source code]
- M. Zabihimayvan, R. Sadeghi, D. Doran, M. Allahyari (2019), “A Broad Evaluation of the Tor English Content Ecosystem”, The Web Science conference 2019
- R. Sadeghi, T. Banerjee, W. Romine (2018), “Early hospital mortality prediction using vital signals”, Smart Health, special issue of IEEE/ACM CHASE conference 2018. (Presentation slides / Source code)
- J. Hamidzadeh, M. Zabihimayvan, R. Sadeghi (2018), “Detection of Web site visitors based on fuzzy rough sets”, Soft Computing, 22(7), 147-158, April 2018. (Impact factor: 2.472)
- R. Sadeghi, J. Hamidzadeh (2018), “Automatic support vector data description”, Soft Computing, 22(1), 147-158, January 2018. (Source code) (Impact factor: 2.472)
- M. Zabihimayvan, R. Sadeghi, H. NathanRude, D. Doran (2017), “A soft computing approach for benign and malicious web robot detection”, Expert Systems with Applications, 87, 129-140, November 2017. (Source code) (Impact factor: 3.928)
- J. Hamidzadeh, R. Sadeghi, Neda Namaei (2017), “Weighted support vector data description based on chaotic bat algorithm”, Applied Soft Computing, 60, 540-551, November 2017. (Impact factor: 3.541)
- A. Gholinezhad Devin, K. Abedzadeh Ghuchani, R. Sadeghi , H. Koosha (2015), “Dynamic Facility Location with Stochastic Demand” , Shiraz Journal of System Management, 3:3, 77-90, Fall 2015.
- A. Gholinezhad Devin, K. Abedzadeh Ghuchani, R. Sadeghi (2013), “Stochastic Facilities location Model by Using Stochastic Programming”, Shiraz Journal of System Management, 1:4, 59-71, October 2013.
Research Service
- Dissertation / Thesis committee member
- Title: Novel Natural Language Processing Models for Medical Terms and Symptoms Detection in Twitter
- Year and Degree: 2022, Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Wright State University, Computer Science and Engineering PhD.
- Role: External Committe member
- Journal reviewer
- Pattern Recognition
- Knowledge-Based Systems
- IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems
- Journal of Big Data
- Journal of Medical Internet Research
- International Journal of Science and Business
- International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
- Conference program committee & external reviewer
- The 2022 IEEE / WIC / ACM International Joint Conferences on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology
- ML4H: Machine Learning for Health 2021
- The 6th edition of the International conference on Time Series and Forecasting (ITISE 2019)
- IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI'19)
- International Conference on Automation, Control and Robots 2019 (ICACR 2019)
- IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems 2019 (FUZZ-IEEE 2019)
- Computing Conference 2019
- Intelligent Systems Conference (IntelliSys) 2019
- IEEE International Conference on Big Data (IEEE Big Data 2018)
- The Web Conference 2018
- International Conference on Automation, Control and Robots 2018 (ICACR 2018)
- The Biomedical Research Conference 2018
- Academic outreach coordinator
- Biomedical Research and Technology Association
- Student volunteer
- SIGIR conference, Ann Arbor, MI (2018)
Education
- Ph.D., Computer Science 2020
- Wright State University, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Kno.e.sis Research Center, Dayton, OH, USA
- Dissertation: Predicting Subjective Sleep Quality Using Objective Measurements in Older Adults
- Advisor: Dr. Tanvi Banerjee
- M.S., Computer Engineering- Software 2015
- International Imam Reza University, Department of Computer and Information Technology, Mashhad, Iran
- Thesis: Strengthening Support Vector Classifiers against Outliers using Fuzzy Rough Set and Evolutionary Methods
- B.S., Computer Engineering- Software, 2012
- Isfahan University of Technology (IUT), Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Isfahan, Iran
- Project: Designing & implementation of online library management website in IUT High School
Frequently Questioned Answers
- How can I take a research-based course or an independent study credite with you?
- You must earned an A in one of my courses to take any research-based courses with me.
- How can I become a member of AI-health for all research group ?
- Send an email with the title of "AI-health for all research group" that contains your resume, your research interest, your availability, and a time spot from research group office hours
- What should I do if you are in my thesis committee?
- Please submit your thesis draft at least two weeks before your thesis defense.